Kingdom of England


![Ver [Ailes, A.; 1982] en referencias bibliográficas. Libro abierto, hojas de plata, filo de oro, guardas de gules, tapas de sable.](../css/Libro.Bibliografia.png)
Ailes, A.; 1982

Adrian Ailes, «The Origins of the Royal Arms of England: Their Development to 1199», foreword by Rodney Dennys, includes 27 black and white illustrations, Graduate Centre for Medieval Studies, Reading University, 126 pages, ISBN 07-049077-6-3, Reading, Berkshire, 1982.
An article reviewing this book is: Brigitte Bedos Rezak, Archives nationales de Paris and Metropolitan Museum of Art, «The Origins of the Royal Arms of England, their Development to 1199 by Adrian Ailes», Speculum, volume 60, number 2, pages 373-376, Medieval Academy of America, Cambridge, Massachusetts, April of 1985.
Bibliographical reference of century XX.
Author: Ailes, Adrian.
Bibliographical reference mentioned in the following article:
External resource:


Aldam, lineage of England

Blazon of the Aldam lineage of England.
Azure, a ray of the sun bendwise, issuant from the dexter chief Or.
Escudo de azur, un rayo de sol puesto en banda, naciente de la diestra del jefe de oro.
Illuminated with lights and shadows and with a freehand finish.
Described in [Burke, B.; 1989; page 9, column 1, entry 11].
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Azure, One, Ray of the sun, Bendwise, Nascent, Dexter, Chief and Or.
Style keywords: Freehand, Outlined in sable, Illuminated and Semi-circular.
Classification: Interpreted, Lineage and Kingdom of England.


Boteler of Warrington

Azure, a bend between six covered cups Or.
Escudo de azur, una banda acompañada de seis copas todo de oro.
Illuminated with lights and shadows and with a freehand finish.
Around 1155, Beatrix de Villers married Richard le Boteler Pincerna, who became the 4th Baron of Warrington. The heir of Beatrix and Richard took the surname «le Boteler» and ruled the Warrington region, bearing arms Azure, a bend between six covered cups Or.
In Castilian, a «copa» has a lid and is referred to as a «covered cup» in English. When it doesn't have a lid, it's called a «cup» in English and a «cáliz» or «copón» in Castilian, the latter being a less preferred term for me. In English, the term «chalice» is also used, especially if it's adorned with gemstones, although that's more of an artistic license.
Naipes Heraclio Fournier is a renowned Spanish playing card manufacturer based in Villareal de Álava. The countless hours I have spent holding its cards in my hands are incalculable, whether playing with friends, opponents, or performing magic tricks. Its influence on my heraldic artwork is significant. For instance, in this covered cup.
The following image shows my covered cup and my two interpretations of his arms: 1) the most commonly viewed, and 2) my alternative layout.
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Azure, One, Bend, Between, Six, Covered cup and Or.
Style keywords: Freehand, Outlined in sable, Illuminated and Semi-circular.
Classification: Interpreted and Kingdom of England.
Bearer: Boteler of Warrington.


![Ver [Charles' Roll; 1285] en referencias bibliográficas. Libro abierto, hojas de plata, filo de oro, guardas de gules, tapas de sable.](../css/Libro.Bibliografia.png)
Charles' Roll; 1285
«Charles's Roll», containing 486 painted coats of arms, it is an English roll of arms dating from c. 1285.
Charles' Roll, housed in the Society of Antiquaries, London, and cataloged as MS517, is a 15th-century English roll of arms, originally created around 1285, containing 486 painted coats of arms. The antiquary James Robinson Planché identified «Charles's Roll» as a copy of a mid-13th-century roll, British Library, Harley MS 6589, featuring nearly 700 coats of arms, drawn by Nicholas Charles, Lancaster Herald, in 1607. Charles mentioned that the original roll had been lent to him by the Norroy King of Arms.
Bibliographical reference of century XIII.
Classification: Armorial roll, Manuscript and In color.
The author is anonymous.
The following articles cite this bibliographic reference:


Edmund Plantagenet

The one with the Cross on his back ~ Crouchback (1245–1296)
Arms of England; overall, a label Azure of three points, each charged with three fleurs-de-lis Or in pale.
Arms interpreted as follows: the mouth of the shield is semicircular (round); the field enamelled in a flat tint of Gules; the label and figures illuminated in Or and Azure and outlined in Sable; and the whole finished with a watercolour effect.
He was the second son of King Henry III of England, and took part in the Ninth Crusade, hence the epithet «Cross on the back».
In 1253 he was appointed Earl of Chester, holding dominion, among others, over the county of Cheshire, but the following year Pope Innocent IV granted him the crown of Sicily, so he ceded his earldom to his elder brother Edward I of England, however, he never came to occupy the throne of Sicily.
The label is an honourable ordinary and also «a kind of mark of cadency, and the most noble of all those used to differentiate the Arms of the younger sons of a House» [Avilés, J.; 1725a; page 248] and it can likewise be used by the eldest son while his father's arms are still in use, ceasing to bear the label when he inherits his father’s coat. When both the eldest and the second son bear a label, the latter’s label then has more points or is charged with figures to distinguish it.
The label is constructed with «a fillet, which is one-ninth of the width of the chief, with three pendants in the form of carpentry wedges or ill-shaped triangles, joined to it without any line of separation, falling twice as far as the fillet is wide, two placed at the ends and one in the middle, its usual position being in the centre of the chief’s length, without reaching the edges of the shield» [Avilés, J.; 1725a; page 248].
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Gules, Or, Azure, Three, Leopard, Armed, Langued, In pale, Surmounted, Overall (deprecated), Label, Suspended, Charged and Fleur de lis.
Style keywords: Semi-circular, Illuminated, Outlined in sable and Watercolor.
Classification: Interpreted, Personal, Coat of arms, House of Plantagenet and Kingdom of England.
Bearer: Edmund Plantagenet.


Edward II of England

First Prince of Wales from 1301 to 1307, King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1307 to 1327.
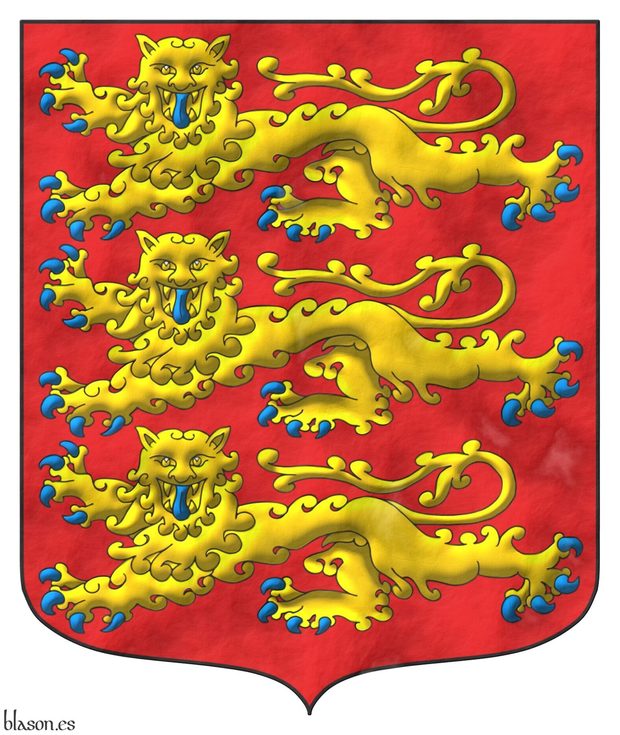
Gules, three lions, passant, guardant, in pale Or, armed and langued Azure.
Escudo de gules, tres leopardos en palo de oro, armados y lampasados de azur.
Coat of arms interpreted as follows: the mouth rounded; the field illuminated Gules; the figures illuminated in Or and Azure, outlined in Sable, and the third leopard slightly smaller; and the whole finished with a plastered effect.
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Gules, Or, Azure, Three, Leopard, Armed, Langued and In pale.
Style keywords: Rounded, Illuminated, Outlined in sable and Gesso.
Classification: Interpreted, Personal, Coat of arms, House of Plantagenet and Kingdom of England.
Bearer: Edward II of England.


Edward IV of England
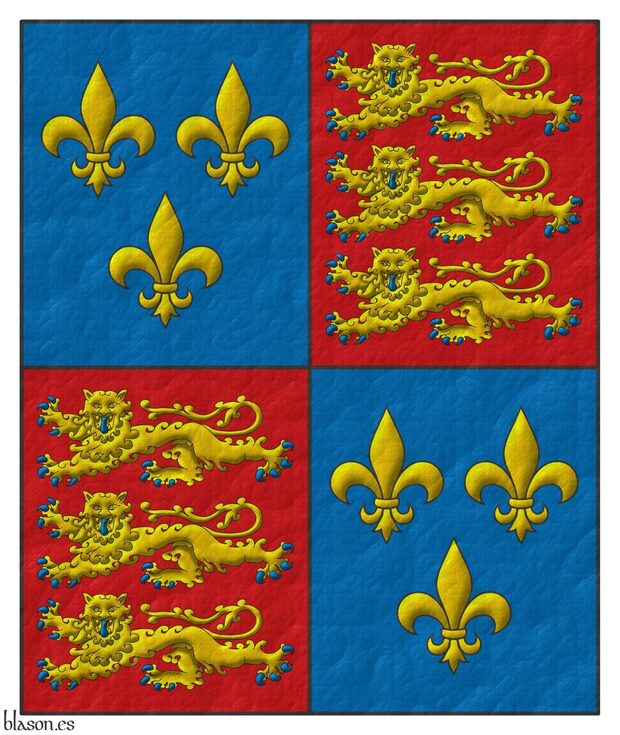
Banner Quarterly: 1 and 4 Azure, three fleurs de lis Or; 2 and 3 Gules, three lions, passant, guardant, in pale Or, armed and langued Azure.
Pendón cuartelado: 1o y 4o de azur, tres flores de lis de oro; 2o y 3o de gules, tres leopardos en palo de oro, armados y lampasados de azur.
Banner interpreted by me as follows: with the proportions of 5x6, like a shield; the field is coloured in flat tinctures Gules and Azure; the fleurs-de-lis and the leopards are outlined in Sable and illuminated in Or; and the banner’s finish resembles fabric.
Its design follows [Edward IV of England; 1461; row 27, 2nd column, final banner]:
- which represents what are considered «the royal arms of England»,
- which were also borne by Henry V of England,
- which Henry VI of England placed in the 2nd quarter of a per pale shield, where he set those of France in the 1st, and
- which were restored by Henry IV, as shown here.
Blazon keywords: Quarterly, Azure, Or, Three, Fleur de lis, Ordered, Gules, Leopard, Armed, Langued and In pale.
Style keywords: Rectangular, Illuminated, Outlined in sable and Fabric.
Classification: Interpreted, Personal, Flag, Banner of arms, Kingdom of England and House of York.
Bearer: Edward IV of England.


![Ver [Edward IV of England; 1461] en referencias bibliográficas. Libro abierto, hojas de plata, filo de oro, guardas de gules, tapas de sable.](../css/Libro.Bibliografia.png)
Edward IV of England; 1461
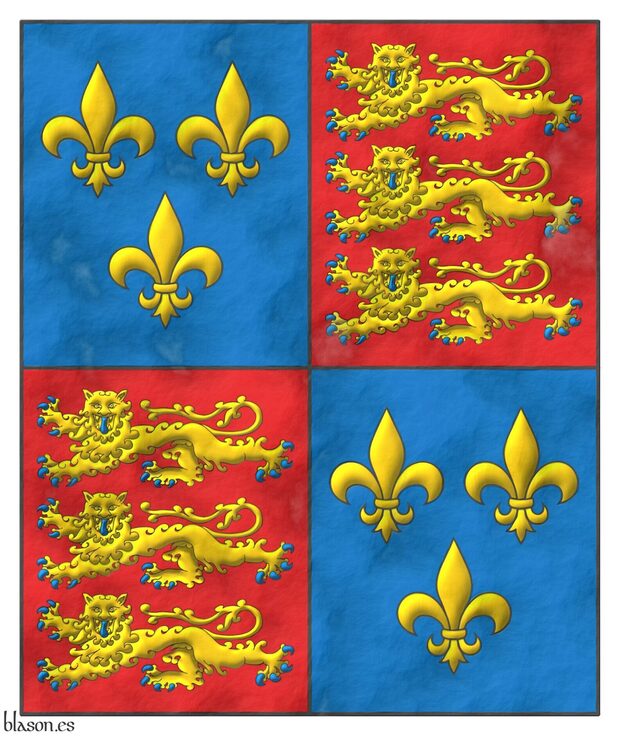
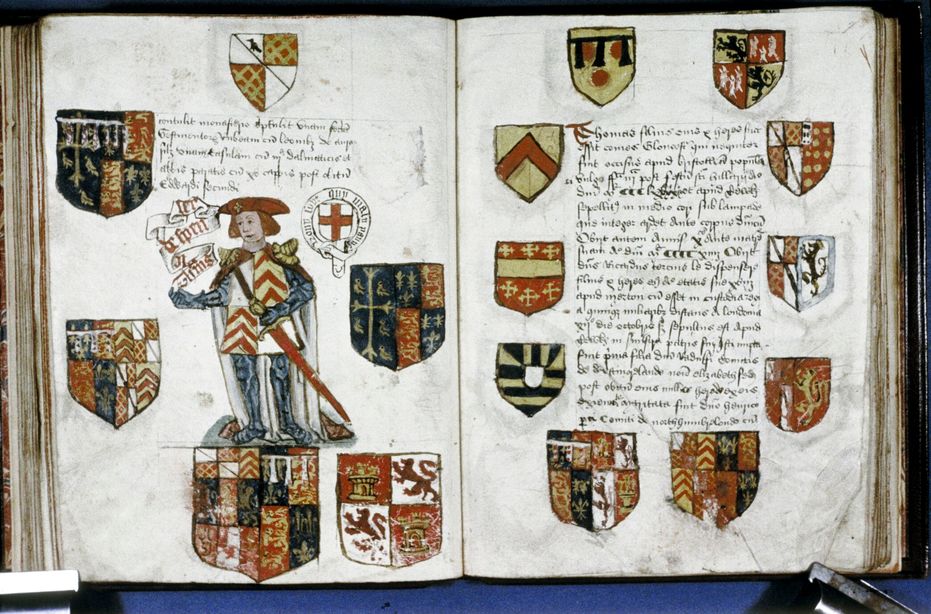
Edward IV King of England and Lord of Ireland, «The Armorial of Edward IV», «The Edward IV Roll», armorial in the form of a roll about 6 meters long, created to celebrate the coronation of Edward IV as the first King of England from the House of York and illustrated, probably, by different artists, 1461.
The image illustrating this reference corresponds to the banner, which is number 27 in the 2nd column, the final one of this armorial. This banner is held by a white deer, which was a personal badge of King Richard II of England, and also, two white deer were the supporters of his shield. The reason for the inclusion of this white deer might be to contribute to the legitimization of Edward IV as king.
It is notable that in row 25 of the 2nd column of this armorial there is a banner with the arms of the shield of Castilla y León, probably because Edward IV, like his predecessors, claimed their throne. In this version of the shield of Castilla y León:
- The two gold castles, in the 1st and 4th quarters of gules, have three towers with the central one taller like the Castilian, but the twin side towers seem to be connected by the wall as in the English castle, [Valero de Bernabé, L.; 2009a; page 2] and [Valero de Bernabé, L.; 2009b; page 33], the wall has a door that is enameled in azure as in the Castilian.
- The two lions, in the 2nd and 3rd quarters of silver, seem to be gold, therefore, of «metal on metal» and, furthermore, very different from the purple lion of Castilla y León, it could well be an error by the artist or a degradation of an original purple enamel to ochre, as explained in the pendón de Castilla y León.
This shield of Castilla y León also appears:
- On the banner in row 27 of the 1st column of this armorial. In this banner, they are combined with the arms of England represented in this article, in a new quartered, under an escutcheon with the imaginary arms of «Brutus of Troy», the also imaginary founder and king of Britain.
- On the caparison of the horse that Edward IV rides in the portrait at the beginning of his armorial. This caparison is a reproduction of the previous banner in row 27 of the 1st column that combined the arms of England with those of Castilla y León. The presence of these arms in this initial portrait of the armorial of Edward IV denotes the importance he gave to his aspirations to the crown of Castilla y León.
Bibliographical reference of century XV.
Author: Edward IV of England.
The following articles cite this bibliographic reference:
- Banner of Castile and León
- Brutus of Britain
- Brutus of Britain, banner
- Charles V of France
- Edward IV of England
- Edward IV, armorial for His coronation
- Edward IV, quartered con Castile and León
- Heraldica Nova
- King Arthur, 3 crowns in pale
- King Arthur, banner with 3 crowns in pale
- King Arthur, banner with cross flory
- King Arthur, cross flory
- Leonor de Aquitania
- Pendón con inescutcheon de Edward IV
External resources:


Edward Longshanks

King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307.
Gules, three lions, passant, guardant, in pale Or, armed and langued Azure.
Escudo de gules, tres leopardos en palo de oro, armados y lampasados de azur.
Coat of arms interpreted with the following features: the mouth is semicircular (round); the field enamelled in a flat tint of Gules; the three leopards illuminated in the metal Or and the colour Azure, outlined in Sable, and the leopard closest to the base has a different shape and size; and the whole finished with a fabric-like texture.
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Gules, Or, Azure, Three, Leopard, Armed, Langued and In pale.
Style keywords: Semi-circular, Illuminated, Outlined in sable and Fabric.
Classification: Interpreted, Personal, Coat of arms, House of Plantagenet and Kingdom of England.
Bearer: Edward I of England.


Grenville, Thomas

Sir Thomas Grenville II, c. 1453 - c. 1513, Knight of the Most Honourable Military Order of the Bath.
Gules, three Clarions Or.
Illuminated and watercolor finishing.
The clarion is the cadency mark of a ninth daughter in Canadian heraldry.
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Gules, Three, Clarion and Or.
Style keywords: Watercolor, Outlined in sable and Illuminated.
Classification: Interpreted and Kingdom of England.
Bearer: Grenville, Thomas.


Henry II of England

Henry II Plantagenet, King of England, Duke of Normandy, Duke of Aquitaine, Count of Anjou, Count of Maine, and Count of Nantes.
Gules, a lion rampant Or.
Escudo de gules, un león rampante de oro.
Existing arms interpreted by me as follows: the shield's shape is pointed; the field has been enamelled in flat Gules; the lion in Or has been outlined in Sable; and the whole composition has a rough texture finish.
It is believed that Henry I was the first King of England to have a coat of arms, featuring a single lion rampant, but no documentary evidence has yet been found [Rabbow, A.; 1999; paragraph 8].
[Ailes, A.; 1982; page 62] argues that Henry II may have used three different versions of his arms featuring a) a single lion rampant, b) two leopards, and c) three leopards. However, it remains unclear whether these versions were used sequentially over time or concurrently. For this interpretation, I have chosen the version with the lion rampant.
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Gules, One, Lion, Or and Rampant.
Style keywords: Pointed, Plain tincture, Outlined in sable and Rough.
Classification: Interpreted, Coat of arms, Personal, House of Plantagenet and Kingdom of England.
Bearer: Henry II of England.


Henry III of England
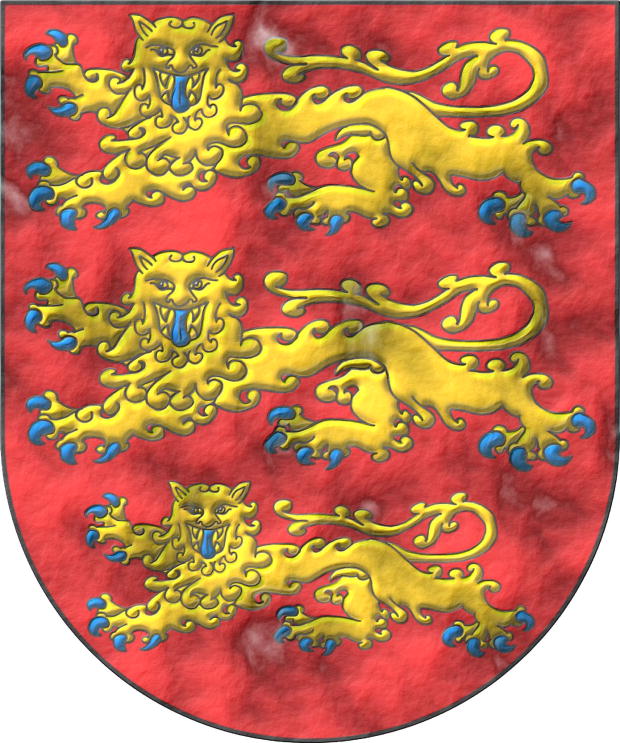

King of England, Lord of Ireland and Duke of Aquitaine from the year 1216 to the year 1272
Gules, three lions, passant, guardant, in pale Or, armed and langued Azure.
Escudo de gules, tres leopardos en palo de oro, armados y lampasados de azur.
Coat of arms interpreted as follows: the mouth of the shield is semicircular (round); its field has been enamelled in a flat tint of Gules; its leopards are illuminated in Or and Azure and outlined in Sable; and the whole has a finish of aged parchment.
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Gules, Or, Azure, Three, Leopard, Armed, Langued and In pale.
Style keywords: Semi-circular, Illuminated, Outlined in sable and Old parchment.
Classification: Interpreted, Personal, Coat of arms, House of Plantagenet and Kingdom of England.
Bearer: Henry III of England.


![Ver [Heralds' Roll, T.; 1280] en referencias bibliográficas. Libro abierto, hojas de plata, filo de oro, guardas de gules, tapas de sable.](../css/Libro.Bibliografia.png)
Heralds' Roll, T.; 1280
«The Heralds' Roll», containing 697 painted coats of arms, it is an English roll of arms dating from c. 1280.
In The Fitzwilliam Museum, Cambridge, with code MS297, there is a copy of the 15th century.
Bibliographical reference of century XIII.
Classification: Armorial roll, Manuscript and In color.
The author is anonymous.
Bibliographic reference mentioned in the following articles:
External links:


![Ver [Humphery-Smith, C.; 1983] en referencias bibliográficas. Libro abierto, hojas de plata, filo de oro, guardas de gules, tapas de sable.](../css/Libro.Bibliografia.png)
Humphery-Smith, C.; 1983
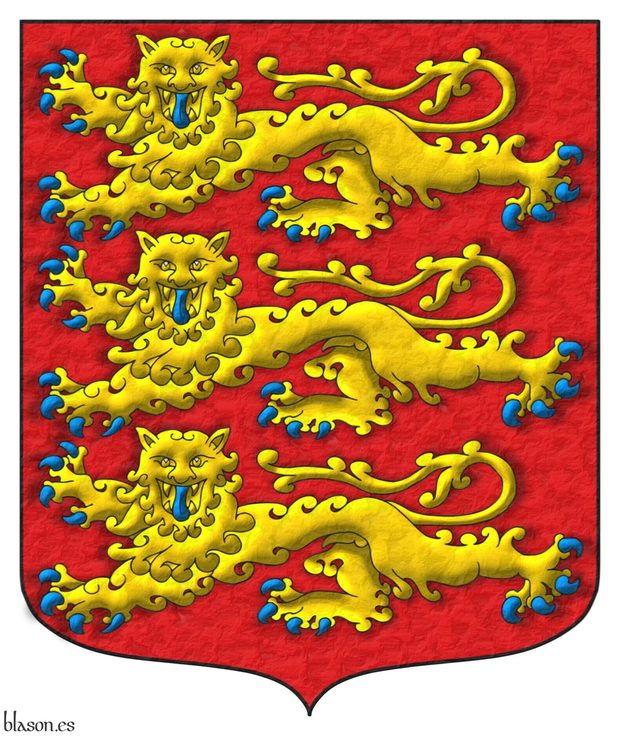

Cecil Humphery-Smith, FHS - Fellow of The Heraldry Society, «Why three Leopards?», Coat of Arms, COA, An Heraldic Quarterly Magazine, issue 126, The Heraldry Society, Baldock, Hertfordshire, summer of 1983.
The coat of arms illustrating this bibliographic reference is that of the Kingdom of England, which was also that of the queen of Castile Leonor Plantagenet.
Bibliographical reference of century XX.
Author: Humphery-Smith, Cecil.
The following articles cite this bibliographic reference:
External resource:
Internal resources: HumpherySmithC1983.3Leopards.docx.


![Ver [Inescutcheon with the arms of Brutus of Britain] en criterios utilizados. Unicornio saltante sobre la divisa, criterio.](../css/Unicornio.Criterio.png)
Inescutcheon with the arms of Brutus of Britain
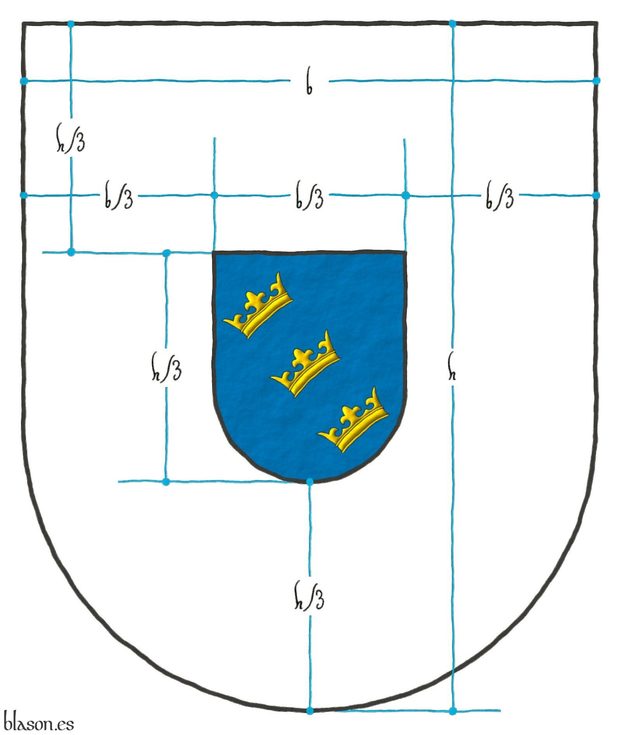
On an inescutcheon Azure, three crowns in bend, bendwise Or.
Escusón de azur, tres coronas en banda, puestas en banda de oro.
Coat of arms interpreted by me as follows: the field is enameled in plain Azure ink; the three crowns are outlined in Sable, illuminated in Or and shaded; and the imaginary shield has a crystalline finish.
Construction process of the inescutcheon of the banner with the inescutcheon of Edward IV from the coat of arms of Brutus of Britain.
Blazon keywords: Inescutcheon.
Style keywords: Illuminated, Semi-circular, Outlined in sable and Watercolor.
Classification: Schema, Interpreted, Imaginary, Kingdom of England and Criterion.
Imaginary bearer: Brutus of Britain.


John Lackland
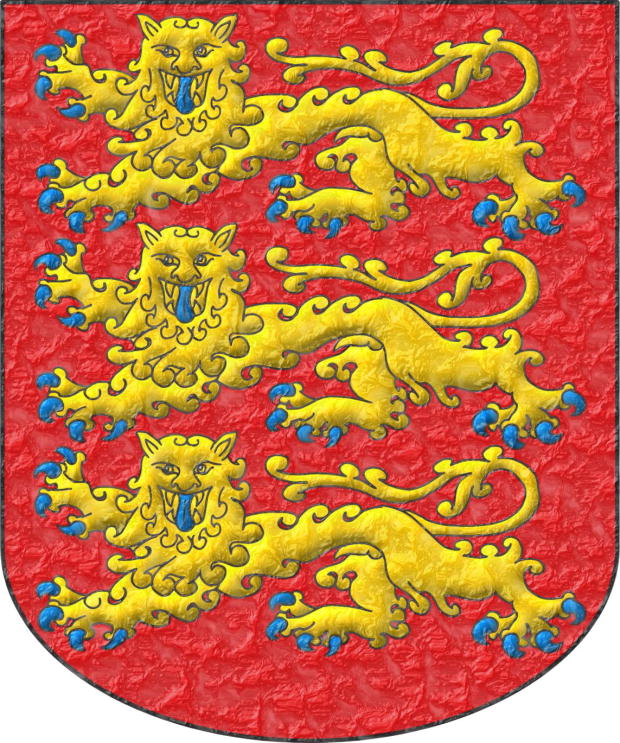

King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1199 to 1216.
Gules, three lions, passant, guardant, in pale Or, armed and langued Azure.
Escudo de gules, tres leopardos en palo de oro, armados y lampasados de azur.
Arms of King John interpreted with: a rounded (semicircular) base; the field enamelled with a flat tint of Gules; the leopards illuminated in Or and Azure, outlined in Sable, all three of the same size; and the whole finished with a crystalline effect.
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Gules, Or, Azure, Three, Leopard, Armed, Langued and In pale.
Style keywords: Rounded, Illuminated, Outlined in sable and Crystalline.
Classification: Interpreted, Personal, Coat of arms, House of Plantagenet and Kingdom of England.
Bearer: John I of England.


King Arthur, cross flory

Arthur Pendragon
Sinople, a cross flory Argent.
Escudo de sinople, una cruz flordelisada de plata.
Imaginary coat of arms interpreted as follows: the mouth of the shield is triangular and curved; the field has been enameled with flat color Vert; the cross flory is illuminated Argent and shaded; and the finish is crystalline.
Its interpretation has been based on the banner that can be consulted in [Edward IV of England; 1461; row 15, 1st column]. Note that King Arthur is represented in this armorial by 2 different arms.
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Vert, Argent, Cross flory and Cross couped.
Style keywords: Illuminated, Shaded, Outlined in sable, Crystalline and Triangular curved.
Classification: Interpreted, Imaginary, Coat of arms and Kingdom of England.
Imaginary bearer: Arthur of Britain.


Leonor de Aquitania y Enrique de Inglaterra
[ Gules, a lion rampant Or, ] accolé with [ Gules, a lion passant, guardant Or ].
[ Escudo de gules, un león rampante de oro, ] acolado de un [ escudo de gules, un leopardo de oro].
Existing arms interpreted by me as follows: both coat of arms are rotated ±30o; their shapes are pointed; the field of each coat of arms has been enamelled in flat Gules; the lion and the leopard in Or are outlined in Sable; and the whole composition of both arms has a rough texture finish.
Examples of accolated coat of arms (written as «accolé» in the 18th century) can be seen in [Avilés, J.; 1780a; pages 24 and 25 and plate 1: figures 1 and 2].
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Gules, One, Lion, Or, Rampant and Leopard.
Style keywords: Pointed, Plain tincture, Outlined in sable, Tilted shield and Metal beaten.
Classification: Interpreted, Personal, Accolé arms, Duchy of Aquitaine, Kingdom of France and Kingdom of England.
Bearer: Leonor de Aquitania.


Leonor Plantagenet and Alfonso VIII
[ Gules, a castle triple towered Or, port and windows Azure, masoned Sable ] accolé with [ Gules, three lions, passant, guardant, in pale Or, armed and langued Azure ].
[ Escudo de gules, un castillo de oro, aclarado de azur, mazonado de sable ] acolado de un [ escudo de gules, tres leopardos en palo de oro, armados y lampasados de azur ].
Arms of the King and Queen of Castile interpreted with: the escutcheons' shapes pointed and rounded; the field of each shield, the castle, and the three leopards enamelled in flat tints of Gules and metal Or, with windows, claws, and tongues in Azure; and the whole composition finished with a raised line technique.
[Medél, R.; 1846; page 38] provides a heraldic description of the leopard.
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Gules, Or, Azure, Three, Leopard, Armed, Langued, In pale, Sable, One, Castle, Port and windows and Masoned.
Style keywords: Ogee, Plain tincture, Outlined in sable, Tilted shield and Freehand.
Classification: Interpreted, Personal, Accolé arms, House of Plantagenet, Kingdom of England and Kingdom of Castile.
Bearer: Leonor Plantagenet.


![Ver [Parsons, R. J.; 1989] en referencias bibliográficas. Libro abierto, hojas de plata, filo de oro, guardas de gules, tapas de sable.](../css/Libro.Bibliografia.png)
Parsons, R. J.; 1989
Robert John Parsons, heraldic painter at the College of Arms, «The Herald Painter», is an article derived from the lecture given by R. J. Parsons at The Heraldry Society on January 18, 1989, at the premises of «The Society of Antiquaries» at Burlington House, London, and later published in Coat of Arms, COA, An Heraldic Quarterly Magazine, issue 146, The Heraldry Society, Baldock, Hertfordshire, summer of 1989.
This article presents a historical review of the heraldic painters at the «College of Arms» and analyzes the creation of coats of arms and other objects like badges, flags, stained glass, seals, etc. It is especially interesting for its view of the current stage of heraldic art and, even more, the description of the author's own working method.
I highly recommend reading this article and, here, I present some of the ideas that I highlighted while studying this text by R. J. Parsons, who is «herald painter to Her Majesty's College of Arms».
Tradition and innovation in heraldic art
Creativity, innovation, and achieving a unique style are fundamental characteristics of any self-respecting artist, but when artists enter the realm of heraldry and, especially when working for institutions like the College of Arms, the weight of the norms and rules of heraldry, its long historical tradition, the reverential respect towards it, the language of blazon, the need for a long initiation process, etc. can cause artists to curb their natural impulses, become intimidated, and adhere strictly to rules to avoid criticism, which hinders the introduction of new proposals, ideas, and styles, risking making heraldry a static and time-bound field.
R. J. Parsons' working method
Robert Parsons explains that the first phase of his method is to create the complete drawing of the coat of arms and its ornamentation on tracing paper, starting with the coat of arms and then outlining all the external ornamentation.
He does this considering that the main problem he must solve is reconciling the two-dimensionality of the coat of arms with the three-dimensionality of the external ornamental elements, such as the supporters, mantling, crest, etc. which must be designed as if enveloping the coat of arms. The extent to which this is achieved provides an idea of each artist's skill.
Silhouettes, expressiveness, and balance
R. J. Parsons believes that the silhouettes of the figures probably characterize each artist and their designs the most. For him, each silhouette must be bold and express emotions, and the silhouettes must maintain proportions that give balance to the whole, as there are no rules that guarantee a good aesthetic result.
To achieve boldness and expressiveness in the figures, especially in natural ones, the artist must emphasize certain features and stylize others, resulting in, for example, in beasts and birds, representations that diverge from natural reality.
Shape of the coat of arms and space
All delineation must be done within the chosen mouth shape for the coat of arms. These shapes have evolved over time, and the artist must consider that some shapes facilitate the internal composition of the coat of arms more than others. For example, he highlights the difficulty of fitting the pieces and figures within lozenge-shaped shields, traditionally carried by unmarried women.
Regardless of the chosen shape, pieces and figures must be arranged to use the entire internal space correctly, neither too small to leave space nor too large to make the whole crowded.
External ornamentation
Robert J. Parsons observes that nowadays the protocol rules that used to govern external ornamentation have been greatly relaxed, for example, regarding the shapes, positions, and orientations of the helmets depending on who would be the holder of the coat of arms, and this relaxation has favored art, aesthetics, and the balance of the whole coat of arms.
He states that of all the external ornamentation, and many heraldic artists will agree with him, the most complex to create are the supporters and tenants, and of the three, the tenants, i.e., human figures, are the most difficult.
Human figures do not have a proper heraldic characterization as lions, unicorns, boars, etc., do. The characterization of women and men in heraldry is done through their attire and the objects they carry or accompany them, with ancient attire and objects being the easiest to characterize, while the more modern and, even more so, the more naked they are, the more difficult and challenging it becomes to create heraldically attractive tenants.
As a general rule, Parsons advises that the visual weight of supporters, tenants, and tenants be similar to that of the coat of arms, so that they neither draw all the observer's attention due to their excessive size nor look ridiculous and incapable of performing their function, which is to support the visual weight of the coat of arms.
Tinctures, shadows, edges, and highlights
When he finishes the drawing phase, R. J. Parsons explains how he transfers it to a new paper support and, then:
- he starts by applying the tinctures for the metals,
- the first he applies is gold using gold powder, although it is known that other artists use gold leaf,
- then the metal silver is left as the white of the paper,
- then he proceeds with the colors, using gouache, an opaque watercolor, following the order from light to dark,
- so the first color he applies is gules, which he tends to make somewhat translucent,
- then the mid-tones, azure and vert.
- ending with sable, which he makes warmer with a touch of burnt sienna,
- after applying the tinctures, he adds shadows to suggest forms, noting that some schools say everything should be in flat inks, without shadows or highlights, and even without delineated edges as can be seen, for example, in Norsk Heraldisk Forening,
- then he delineates the silhouettes and
- finishes by adding highlights to bring the composition to life.
The motto or slogan is the last element with which Robert John Parsons completes the creation of a coat of arms.
Bibliographical reference of century XX.
Author: Parsons, Robert John.
Bibliographical reference mentioned in the following article:
External link:
Internal resources: ParsonsRJ1989.TheHeraldPainter.docx.


Richard I of England
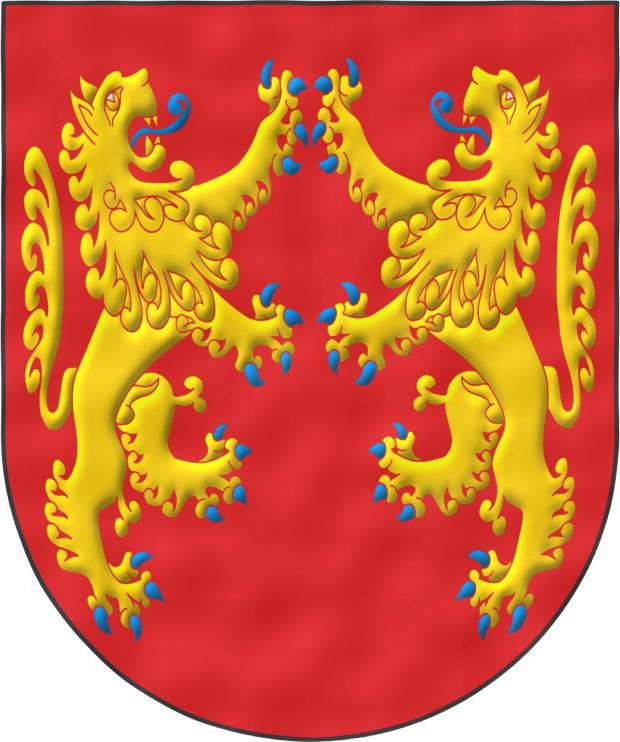
Lionheart ~ Corazón de León ~ Cœur de Lion.
Escudo de gules, dos leones de oro, afrontados, armados y lampasados de azur.
Coat of arms interpreted as follows: the mouth drawn as a semicircular (round) base; the field enamelled in a flat tint of Gules; the two lions outlined in the colour of the field and illuminated in Or and Azure; and the whole finished with a watercolour effect.
He was born in 1157, being the third of eight children of Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine, elder brother of Eleanor Plantagenet. He was king of England between 1189 and 1199, although he spent much of his life far from it; in fact, during his ten-year reign, he was on English soil only twice, which together did not amount even to six months. He died in 1199 in Normandy.
In 1198, during the Battle of Gisors, he supposedly used, as watchword or as motto, the expression «Dieu et mon Droit ~ God and my right». This phrase refers to his refusal to bow before Emperor Henry VI, since by his rank Richard acknowledged only God as superior. Later, Henry V of England adopted it as his motto, and since then it has been used by the British monarchy.
According to [Humphery-Smith, C.; 1983], Richard the Lionheart was the first English king who can be proved to have borne arms, although some of his predecessors may also have had them. He bases his statement on the existence of two seals of Richard I: on one, Richard bears a shield with a rampant lion, and on the other there already appear the three lions that are the forerunners of the arms of England. The use of this second seal does not imply that he stopped using the first.
In contrast, there are also British authors who maintain that his shield actually bore two affronted lions; this hypothesis is based on the lion on his first seal facing to sinister. That latter hypothesis is the one interpreted in this shield, remaining a purely artistic interpretation and without my entering into a complex and open discussion about how, when, and why the three leopards, «leones pasantes ~ lions passant» for the English, appeared —a discussion in which there are various alternatives— ranging from the combination of his hereditary arms to the wish to have more lions than his younger brother, who would later be King John I of England, to possible influences from other European realms.
This version of Richard I’s shield is similar to the imaginary shield of Hector of Troy, Gules with two lions Or affronté, which is a term used when «two things are placed facing each other, like two Lions, two Dogs, or other animals that look at one another» [Avilés, J.; 1725a; page 32].
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Gules, Lion, Or, Combatant, Armed, Langued and Azure.
Style keywords: Semi-circular, Illuminated, Outlined in sable and Freehand.
Classification: Interpreted, Personal, Coat of arms, House of Plantagenet and Kingdom of England.
Bearer: Richard I of England.


![Ver [Scott-Giles, C. W.; 1965] en referencias bibliográficas. Libro abierto, hojas de plata, filo de oro, guardas de gules, tapas de sable.](../css/Libro.Bibliografia.png)
Scott-Giles, C. W.; 1965

Charles Wilfred Scott-Giles, OBE (Officer of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire), Fitzalan Pursuivant Extraordinary, «Some Arthurian Coats of Arms», Coat of Arms, COA, An Heraldic Quarterly Magazine, issue 64 of October 1965 (which is the date I use as reference) and issue 65 of January 1966, The Heraldry Society, Baldock, Hertfordshire, October 1965.
The coat of arms illustrating this bibliographic reference is one of the variants described in this article attributed to King Arthur, which in Blason.es is cataloged as Arthur of Britain.
Bibliographical reference of century XX.
The author is Scott-Giles, C. W..
The following articles cite this bibliographic reference:
External resource:
Internal resources: ScottGilesCW1965.SomeArthurianCoA.docx.


Sir Robert Knollys (1325-1407), first post

Sir Robert Knollys ~ Sir Robert Knolles (1325-1407).
Gules, on a chevron Argent three roses Gules, barbed Vert, and seeded Or.
Escudo de gules, un cabrio de plata cargado de tres rosas de gules, barbadas de sinople y botonadas de oro.
Coat of arms interpreted with: the rounded form; the field illuminated in Gules; the chevron illuminated in Argent metal and outlined in Sable; the roses illuminated in Gules, Vert and Or and outlined in Sable; and the whole with a raised-stroke effect.
Sir Robert Knollys was an English man-at-arms who was born in the County of Cheshire in 1325 and died in Sculthorpe, Norfolk, in 1407, and whose military career was framed within the Hundred Years' War between England and France.
Blazon keywords: Without divisions and Gules.
Style keywords: Rounded, Illuminated, Outlined in sable and Freehand.
Classification: Interpreted, Personal, Kingdom of England and Army and Navy.
Bearer: Knollys, Robert.


![Ver [St. George's Roll; 1285] en referencias bibliográficas. Libro abierto, hojas de plata, filo de oro, guardas de gules, tapas de sable.](../css/Libro.Bibliografia.png)
St. George's Roll; 1285

St. George's Roll, in English usually written as «MS Vincent, 164 ff.1-21b», also called [Vincent, MS; 1285], it is in the College of Arms, London, containing 677 painted coats of arms, it is an English roll or arms dating from c. 1285.
The bibliographical reference that I mainly use for this armorial is [Vincent, MS; 1285].
Bibliographical reference of century XIII.
Classification: Armorial roll and Manuscript.
The author is unknown.
Bibliographic reference mentioned in the following articles:
- Adam de Cretingges
- Bartholomew de Yattendon
- Brian Timms
- Edmund de Bassingburnn
- Howel ap Res
- James de Sottone, le Fitz
- Joan de Okinton
- John de Beauchamp
- John de Ladbrooke
- John le Sturmy
- Nicholas Malmains
- Norman Darcy
- Ricardo de Mandeville
- Robert de Malet
- Simon de Crombe
- Simon de Ver
- Simon le FizSimon
- Thomas Roscelyn
- Thomas de Werblintone
- Thomas le FizThomas
- Vincent, MS; 1285
- Warbrentone, Thomas de
- William Bardolf
- William de Ferrers, Earl of Derby
- William de Hondeshacre


Talbot, lineage of England

Blazon of the Talbot lineage of England.
Escudo de gules, un león rampante dentro de una bordura angrelada todo oro.
Gules, a lion rampant within a bordure engrailed Or.
Illuminated with lights and shadows and with a freehand finish.
[Rietstap, J. B.; 1861] writes it in French as «de gueules, au lion d'or, à la bordure engrelée du même». y [Burke, J.; 1836; volume 3, pages 359-360] writes it in English as «Gu. a lion rampant, within a bordure engr. or».
Blazon keywords: Without divisions, Gules, One, Lion, Rampant, Within, Bordure, Engrailed and Or.
Style keywords: Freehand, Outlined in sable, Illuminated and Semi-circular.
Classification: Interpreted, Lineage and Kingdom of England.


![Ver [Tewkesbury; Century XVII] en referencias bibliográficas. Libro abierto, hojas de plata, filo de oro, guardas de gules, tapas de sable.](../css/Libro.Bibliografia.png)
Tewkesbury; Century XVII
Anonymous, «Founder's and benefactors' book of Tewkesbury abbey», Bodleian Libraries, University of Oxford, call number MS. Top. Glouc. d. 2, recorded in the Catalogue of Western Medieval Manuscripts in Oxford Libraries, manuscript, illustrated, 46 leaves, 245 x 175 millimeters, except fols. 12, 16, and 38, which are smaller, Tewkesbury, beginning of the 16th century.
Origin, historical context, and contents
It is is a medieval manuscript originating from Tewkesbury Abbey at the beginning of the 16th century. This Latin manuscript provides records and depictions of the abbey's founders and benefactors, such as: William Fitzcount, 2nd Earl of Gloucester, died 1183; Oddo and Doddo, Dukes of Mercia; Hugh, great Duke of Mercia, lord of the manor of Tewkesbury, buried at Tewkesbury in 812; Robert Fitzhamon, lord of Creully, Calvados in Normandy, died 1107, and his wife, Sybil, patrons of Tewkesbury Abbey’s reconstruction; Edward Despenser, died 1375; Thomas Despenser, Earl of Gloucester, died 1400; and Isabel Despenser, 1400-1439.
Illustrations and manuscript details
The manuscript is noted for its illustrations, which are believed to have been created by John of Evesham, a monk at Tewkesbury. The illustrations are thought to be copied from painted statues, approximately 70 cm high, which once decorated the abbey church. The manuscript comprises 46 leaves, with most pages measuring 245 x 175 millimeters, though folios 12, 16, and 38 are smaller in size.
In the image, folio 25v depicts Thomas Despenser, Earl of Gloucester, in armor, wearing a red bonnet with a badge, and a mantle with epaulettes over a heraldic surcoat. He holds a sheathed sword and is surrounded by six coats of arms and the badge of the Garter with the flag of Saint George; and folio 26r features a text page with ten coat of arms.
Bibliographical reference of century XVII.
Classification: Manuscript, Armorial roll, Latin language and In color.
Author: unknown.
The following article cites this bibliographic reference:
External resource:
Internal resources: 25 images in JPEG format.


![Ver [Vincent, MS; 1285] en referencias bibliográficas. Libro abierto, hojas de plata, filo de oro, guardas de gules, tapas de sable.](../css/Libro.Bibliografia.png)
Vincent, MS; 1285

Vincent Manuscript, in English, usually written as «MS Vincent, 164 ff.1-21b», also called [St. George's Roll; 1285], it is in the College of Arms, London, containing 677 painted coats of arms, it is an English roll of arms dating from c. 1285.
Bibliographical reference of century XIII.
Classification: Armorial roll, Manuscript and In color.
Author: anonymous.
The following articles cite this bibliographic reference:
- Adam de Cretingges
- Bartholomew de Yattendon
- Costa i Cases, P.; Century XVIII
- Edmund de Bassingburnn
- Howel ap Res
- James de Sottone, le Fitz
- Joan de Okinton
- John de Beauchamp
- John de Ladbrooke
- John le Sturmy
- Nicholas Malmains
- Norman Darcy
- Ricardo de Mandeville
- Robert de Malet
- Simon de Crombe
- Simon de Ver
- Simon le FizSimon
- St. George's Roll; 1285
- Thomas Roscelyn
- Thomas de Werblintone
- Thomas le FizThomas
- William Bardolf
- William de Ferrers, Earl of Derby
- William de Hondeshacre
-
Language
-
Categories of heraldry
-
Divisions of the field
- Without divisions
- Party per pale
- Party per fess
- Party per bend
- Party per bend sinister
- Tierce
- Tierce sinister
- Tierced per pale
- Tierced per fess
- Tierced per bend
- Tierced pallwise inverted
- Quarterly
- Quarterly per saltire
- Gyronny
- Party per fess, the chief per pale
- Party per pale, the sinister per fess
- Party per fess, the base per pale
- Party per pale, the dexter per fess
- Chapé
- Chaussé
- Embrassé
- Contre-embrassé
- Party per chevron
- Enté
- Enté en point
- Flanched
-
Metals
-
Colours
-
Furs
-
Other tinctures
-
Ordinaries and sub-ordinaries
-
Diminutives of the ordinaries
-
Geometric charges
-
Composite ordinaries
-
Inanimate charges from Nature
Atom, Crescent, Diamond, Emerald, Estoile, Increscent, Lightning flash, Moon, Mount, Mullet, Mullet of four points, Orbital, Plough of Ursa Major, Rainbow, Ray of the sun, River, Sea, Snowflake, Sun, Sun in splendour, Sun of May, Terrestrial globe, Trimount, Water and Wave.
-
Vegetal charges from Nature
Acorn, Apple, Apple tree, Ash, Bluebonnet, Camellia, Chrysanthemum, Cinquefoil, Cornflower, Dogwood flower, Double rose, Eguzki-lore, Elm, Fleur de lis, Flower, Gourd, Holm oak, Hop cone, Indian paintbrush, Kapok tree, Laurel, Lily, Linden, Lotus flower, Madonna lily, Mexican cedar tree, Oak, Olive tree, Palm tree, Plantain plant, Pomegranate, Poplar leaf, Rose, Shamrock, Sunflower, Thistle, Tree, Tulip, Vine and Wheat.
-
Animal charges from Nature
Badger, Bald eagle, Barbel, Barn owl, Bear, Beaver, Bee, Beetle, Bighorn sheep, Binson, Blackbird, Boar, Brach hound, Bull, Cow, Doe, Dog, Dolphin, Dove, Eagle, Elephant, Falcon, Female figure, Fish, Flame, Fly, Fox, Frog, Goat, Goldfinch, Goose, Heron, Horse, Hummingbird, Jaguar, Lark, Leopard, Lion, Lion passant, Lion rampant guardant, Lioness, Lynx, Male figure, Martlet, Merino ram, Owl, Panther, Parrot, Peacock, Pelican, Pelican in her piety, Pronghorn, Puffin, Quetzal, Raven, Roe deer, Rooster, Savage, Seagull, Serpent, She-wolf, Stag, Starling, Talbot, Turtle, Tyger, Vulture, Warren hound and Wolf.
-
Parts of natural charges
Arm, Beak, Branch, Caboshed, Chest, Claw, Covert, Dorsal fin, Eagle claw, Ear of wheat, Ermine spot, Escallop, Feather, Foot (palmiped), Foreleg, Forepaw, Hand, Head, Heart, Hoof, Leaf, Neck, Ostrich feather, Palm frond, Paw, Roe deers' attires, Shoulder, Sprig, Stags' attires, Stem, Swallow-tail, Tail, Tail addorsed, Tail fin, Talon, Tibia, Tooth, Trunk, Trunk (elephant), Two hands clasped, Two wings in vol, Udder, Wing and Wrist.
-
Artificial charges
Ace of spades, Anchor, Anvil, Arch, Arm vambraced, Armillary sphere, Arrow, Axe, Bell, Bell tower, Beret, Bonfire, Book, Bookmark, Bow, Branding iron, Bridge, Broken, Buckle, Cannon, Cannon dismounted, Cannon port, Canopy roof, Carbuncle, Castle, Celtic Trinity knot, Chain, Chess rooks, Church, Clarion, Clay pot, Closed book, Club, Column, Comb, Compass rose, Conductor's baton, Cord, Covered cup, Crozier, Crucible, Cuffed, Cup, Cyclamor, Dagger, Displayed scroll, Double vajra, Drum, Ecclesiastical cap, Fanon, Federschwert, Fleam, Four crescents joined millsailwise, Galician granary, Garb, Gauntlet, Geometric solid, Grenade, Halberd, Hammer, Harp, Host, Hourglass, Key, Key ward, Knight, Knot, Lantern, Letter, Line, Loincloth, Maunch, Menorah, Millrind, Millstone, Millwheel, Monstrance, Mortar, Mullet of six points pierced, Nail, Non-classic artifact, Norman ship, Number, Oar, Oil lamp, Open book, Page, Pair of pliers, Pair of scales, Parchment, Pestle, Piano, Pilgrim's staff, Plough share, Polish winged hussar, Port, Portcullis, Potent, Quill, Ribbon, Rosette of acanthus leaves, Sabre, Sackbut, Sail, Scroll, Scythe, Sheaf of tobacco, Ship, Skirt, Spear, Spear's head, Stairway, Star of David, Step, Sword, Symbol, Tetrahedron, Torch, Tower, Trident, Trumpet, Turret, Two-handed sword, Wagon-wheel, Water-bouget, Wheel, Winnowing fan and With a turret.
-
Immaterial charges
Angel, Archangel, Basilisk, Dragon, Dragon's head, Garuda, Golden fleece, Griffin, Heart enflamed, Justice, Mermaid, Our Lady of Mercy, Ouroboros, Paschal lamb, Pegasus, Phoenix, Sacred Heart of Jesus, Saint George, Sea-griffin, Sea-lion, Trinity, Triton, Unicorn, Winged hand and Wyvern.
-
External elements
-
Heraldic creations
-
References
-
Formats
-
Keywords on this page
Port and windows, Between, Watercolor, Combatant, Engrailed, Old parchment, Pointed, Armed, Armorial roll, Arthur of Britain, Azure, Bend, Flag, Bibliography, House of Plantagenet, House of York, Crystalline, Quarterly, Outlined in sable, In color, In pale, Fabric, Coat of arms, Accolé arms, Fleur de lis, Personal, Gules, Illuminated, Imaginary, Interpreted, Langued, Leopard, Lion, Lineage, Manuscript, Semi-circular, Ordered, Or, Without divisions, Rampant, Rounded, Kingdom of England, Tilted shield, Century XIII, Century XX, Plain tincture, Freehand, Three and One.


![Leonor de Aquitania y Enrique de Inglaterra [ Gules, a lion rampant Or, ] accolé with [ Gules, a lion passant, guardant Or ].](../escudo_armas/LeonorA.22.EnriqueII.jpg)
![Leonor Plantagenet and Alfonso VIII [ Gules, a castle triple towered Or, port and windows Azure, masoned Sable ] accolé with [ Gules, three lions, passant, guardant, in pale Or, armed and langued Azure ].](../escudo_armas/LeonorP.23.Matrimonio.jpg)
